Technical Data of Organic-Inorganic hybrid Materialss
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
|---|---|
| Color (APHA) | <50 |
| Refractive index | 1.52 |
| Transmittance | >91 % |
| Curing method | thermal or UV-curing |
| Curing shrinkage | <1 % |
| Pencil hardness | >8H (glass substrate) |
- · Soluble in toluene, MIBK, PGMEA, THF and chloroform
- · Curable with anhydrides and amines
- · High thermal stability
- · Increased high use temperature
- · Excellent water and solvent resistance
- · Enhanced thermomechanical performance
Solvent Resistance of Cured Films
[Test Method]
After cured material was immersed into the individual solvent, the change in material appearance between before and after immersion was observed.
| Solvent | Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Materials |
|---|---|
| Color (APHA) | O |
| Alkali | O |
| N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone | O |
| Isopropyl Alcohol | O |
| Methyl Ethyl Ketone | O |
Evaluation Criterion
- · O : No change in appearance
- · △ : Slight change in appearance
- · X : Evident change in appearance
Test Condition
- · Temperature : Ambient
- · Immersion duration : 12hour
- · Acid : 10wt% sulfuric acid aqueous solution
- · Alkali : 10wt% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution
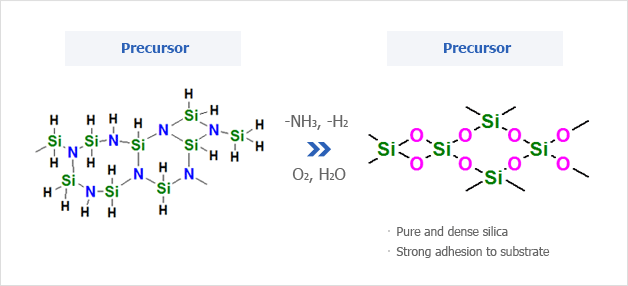
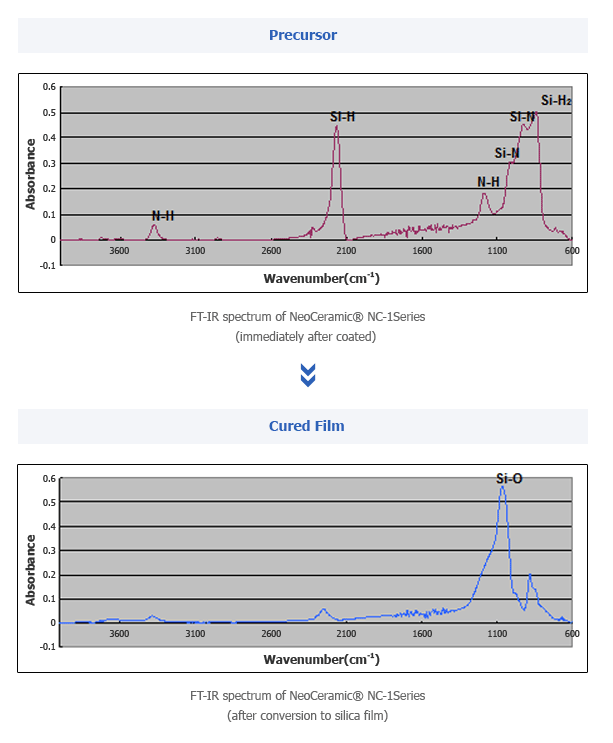
Types of Coatalent Series Coating Solutions
- · Non-catalyst typeHigh temperature baking (e.g., baking at 350°C for 1 hr in air) is required for conversion to silica.This is a basic perhydropolysilazane solution.
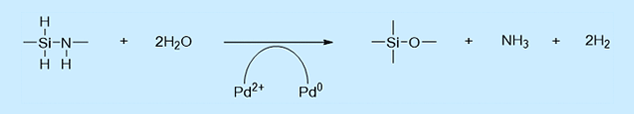
- · Palladium catalyst typeSince palladium is an inorganic catalyst, the coating quality (elaborateness and strength) is superior to amine catalyst type. So, palladium catalyst type is suitable for the corrosion resistance and scratch resistance.This solution is brown but thin coating film after applied is transparent.
- · Amine catalyst typeUsing this grade, conversion to silica is obtained at 150°C for 1 hr, lower temperature than the palladium type and is also produced at room temperature in approx.2 weeks. This type is most suitable for the purpose of anti-soiling coating.