ZymoBIOMICS™ Microbial Community DNA Standard
● Highlights
- A DNA standard of well-defined composition.
- Ideal for the validation, optimization, and quality control of microbiomics and metagenomics workflows.
- The DNA has a wide GC range of 15%-85%.
● Description
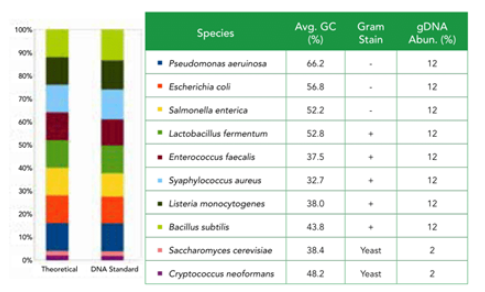
- One of the major challenges in the emerging field of microbiomics is the bias and errors introduced in the complex workflows. Besides nucleic acid purification, bias also arises from sequencing library preparation and subsequent processes. The ZymoBIOMICS® Microbial Community DNA Standard is designed to assess bias, errors and other artifacts after the step of nucleic acid purification. This DNA standard is created by pooling DNA extracted from pure cultures. It has accurately defined composition, negligible impurities (0.01%) and contains genomes of a wide range of GC content (15% - 85%). This DNA standard is designed to have the same microbial composition with the cellular version, the ZymoBIOMICS® Microbial Community Standard, so that they can be more powerful when working in tandem.
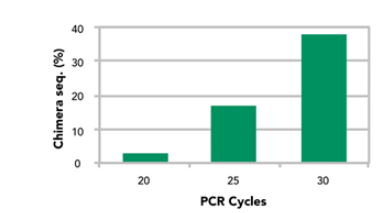
PCR chimera increase the number of PCR cycles during the library preparation process of 16S rRNA gene targeted sequencing. 20 ng ZymoBIOMICS® Microbial Community Standard was used a template. The PCR was performed with ZymoBIOMICS Taq PreMix master mix and with primers that target the v3-4 region of 16S rRNA gene. Chimera percentage was determined with Uchime and using the 16S rRNA genes of the 8 bacterial strains in the standard as reference.
▶ Accurate Characterization
DNA from Gram-negative bacteria, five Gram-positive bacteria, and two tough-to-lyse yeasts. The ZymoBIOMICS Microbial Community Standards are perfect for assessing bias in popular extraction methods The microbial standards are accurately characterized, with a wide GC range (15%-85%) and contain negligible impurities (<0.01%), enabling easy exposure of artifacts, errors, and bias in microbiomics or metagenomic workflows.
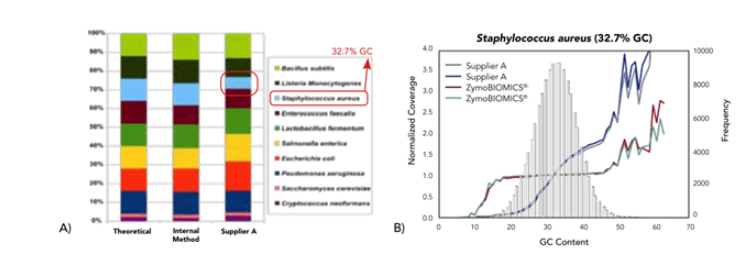
▶ Assess GC Bias &Eliminate It
A) Assessing bias of two different library preparation processes in shotgun metagenomic sequencing using ZymoBIOMICS Microbial Community Standard. Compared to our internal method, the Supplier A kit has some bias due to GC content variation. Sequencing was performed on MiSeq (2 x 150 bp).
B) Raw reads were mapped to the 10 microbial genomes to evaluate the potential effect of GC content on sequencing coverage. Normalized coverage was calculated by normalization with the average sequencing coverage of each genome.